Chapter 8 – Integumentary System Assessment
Introduction to Integumentary System
The integumentary system includes the skin, hair, nails, and and sweat glands. It has important functions including thermoregulation, sensory functioning, ensuring fluid balance, serving as a protective barrier to external substances, and providing immune defense against foreign bodies.
The integument can be an indicator of the client’s general health status. For example, the integumentary system can signal other systemic functions of the body like during cardiac events, related to respiratory insufficiency and other conditions, and during times of stress and other conditions. As a nurse, it is important to hone your assessment skills and pay close attention to potential cues that may signal underlying concerns that require your intervention. See Figure 1 for an anatomical overview of the integumentary system.
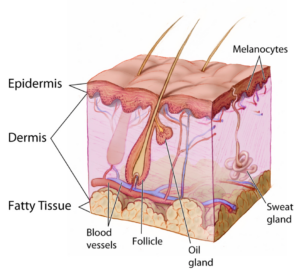
Figure 1: Integumentary system anatomy.
(Image in public domain and adapted from the National Cancer Institute: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anatomy_The_Skin_-_NCI_Visuals_Online.jpg)
You have already learned about the anatomy and physiology of the integumentary system: for a quick overview see https://youtu.be/OxPlCkTKhzY
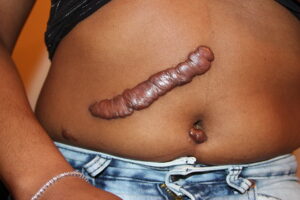
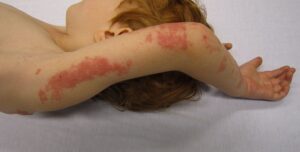
You need a basic understanding of disease-specific presentations to effectively interpret findings from your assessment. Be alert to signs and symptoms of greater systemic issues that may require further assessment and possibly immediate intervention. For example, Cullen’s sign (Figure 2) is a serious concern: it appears as bruising and edema of the subcutaneous fatty tissue around the navel and can be an indication of acute pancreatic trauma and/or internal bleeding. Certain skin symptoms can also prompt the use of personal protective equipment (PPE); for example, small flat red spots that appear on the face and spread down the body may be an indication of (Figure 3), necessitating airborne precautions.
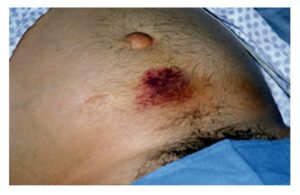
Figure 2: Cullen’s sign.
(Attribution: Photo by Herbert L. Fred, MD and Hendrik A. van Dijk – http://cnx.org/content/m14904/latest/, CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=5038484)
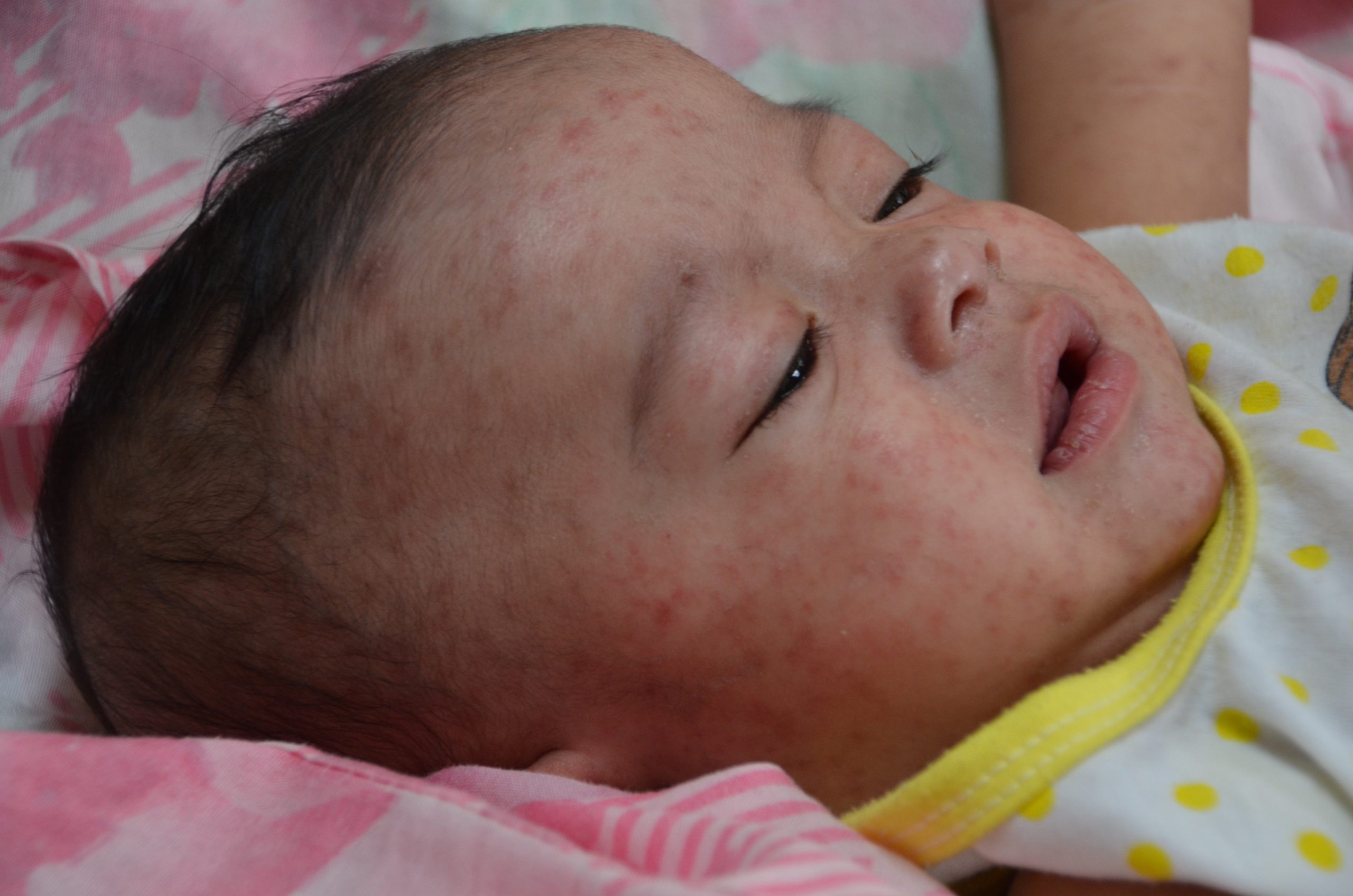
Figure 3: Measles.
(Attribution: This photo is in the public domain in the United States because it is a work prepared by an officer or employee of the United States Government as part of that person’s official duties under the terms of Title 17, Chapter 1, Section 105 of the US Code. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Measles_child_Philippines.jpg)
Contextualization of integumentary issues in relation to other symptomatology like fever, cough, and inflammation can provide insight into underlying conditions. Table 1 provides some general descriptions related to the integument and underlying pathophysiology. With experience, you will learn to identify patterns, recognize cues, and begin to discriminate between skin conditions and skin conditions that require further investigation.
Table 1: General descriptions of integument pathophysiology.
|
Integumentary grouping |
Examples |
Common presentation |
|
Skin trauma Trauma can affect a single or multiple layers of the skin as a result of injury or illness. |
Burns, scars, cuts, tears of the skin, keloids (thick, raised scars).
Keloid. (Attribution: Photo by Htirgan – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org |
Swelling, erythema, inflammation, bleeding, pain, blisters, peeling of skin, and sometimes darkened or lightened areas of skin with scars. |
|
Infections Bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic skin infections are caused by various pathogens and can range from mild to severe. Many skin infections require treatment.
. (Attribution: Photo by James Heilman, MD – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org |
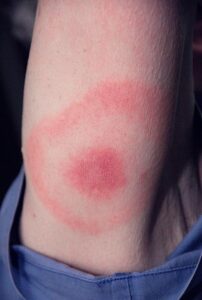
Viral: Human papillomavirus (HPV), herpes zoster virus, warts, COVID-19, shingles. Bacterial: Staphylococcus-aureus, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), impetigo, cellulitis, boils, and abscesses. Fungal (typically skin and mucosal surfaces): Tinea corporis (ringworm), tinea pedis (athlete’s foot), candidosis (yeast infection), nail fungus. Parasitic: Lice, bedbugs. Other stings and bites that can cause infection: Spider bites, ticks, animal bites.
Tick bite with bull’s-eye rash (an early sign of Lyme disease). (Attribution: CDC / James Gathany – https://phil.cdc.gov/Details.aspx?pid=9874, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org |
Viral: Some rashes can follow a (e.g., shingles, varicella, herpes simplex) with lesions, papules, or pain. They can appear in cluster/closely grouped or as a single lesion, and can be generalized, regional, or asymmetrical presentation (i.e., rash on one side of the body). Bacterial: Odour, exudate, small red bumps increasing in size, fever, yellowish-brown crusts, redness, heat, swelling, tenderness, pain. Fungal: Deep erythema, swelling, itchiness, scaly, flaky patches, or loss of normal pigmentation of the skin causing discolouration. Parasitic: Itchiness, rash, regional lymphadenopathy (diseases of the lymph nodes resulting in enlarged lymph nodes). |
|
Auto-immune and/or inflammatory disorders causing lesions/eruptions (acute and chronic) Regional or generalized, may involve inflammation of the skin. |
, , , , , .
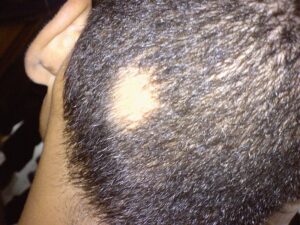
Alopecia. (Attribution: Photo by Abbassyma at English Wikipedia – Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org |
Eczema (scaling, itching, ill-defined), psoriasis (, scaly plaques), vitiligo (depigmentation, patchy loss of skin colour, premature whitening of hair), alopecia (hair loss). |
|
Metabolic and nutritional disorders Poor nutrition or absorption issues can lead to vitamin deficiencies. Excess vitamins can also lead to cutaneous abnormalities. |
Vitamin A, C, D, E, K, B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, B12, iron, zinc, and selenium deficiencies. Vitamin A, E, and selenium excess. |
Varies depending on metabolic/nutritional disorders, e.g., dermatitis, flushing, hyperpigmentation, white spots. |
|
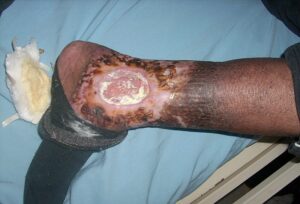
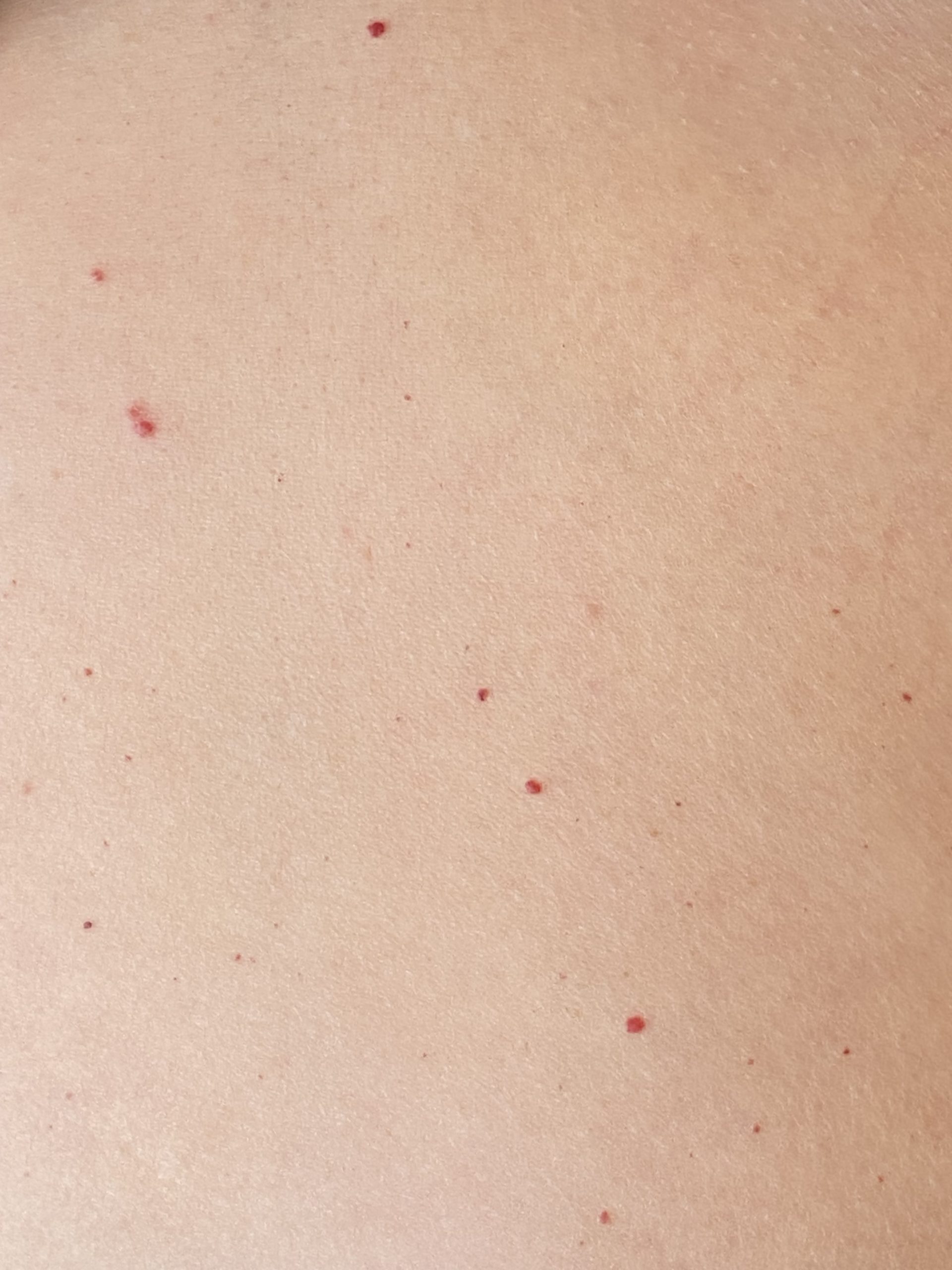
Vascular disorders Cutaneous vascular disorders commonly involve arteries, veins, and/or lymphatic vessels. |
Ulcers, , venous insufficiency.
Venous insufficiency. (Attribution: Photo by Ashashyou – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org
Cherry angioma. |
Varies depending on venous insufficiency (flooding of fluid to the skin due to inadequate venous return) or arterial deprivation (deprivation of nutrients to the skin due to poor arterial perfusion). Variations such as cherry angiomas are not harmful. They can begin small and then grow in size, become slightly raised, and multiply over time. |
|
Psychological and neurological disorders Involve interactions between the mind and skin. |
Persistent and , neuropathic pain (often related to shingles), trichotillomania (a psychiatric condition resulting in compulsive hair pulling). |
Irresistible itching and scratching, urge to scratch exacerbated by anxiety, skin picking, recurrent pulling out of hair. |
|
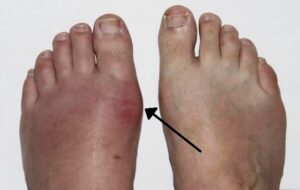
Systemic disorders The integumentary system can be involved in clinical manifestation of some systemic disorders. |
Gout, arthritis, Addison disease, Cushing syndrome, thyroid disease, chronic liver disease, hepatitis, diabetic ulcers. |
Varies depending on the underlying systemic disorder.
Gout. (Attribution: Photo by Gonzos ft – Own work, CC BY 3.0 de, https://commons.wikime |
|
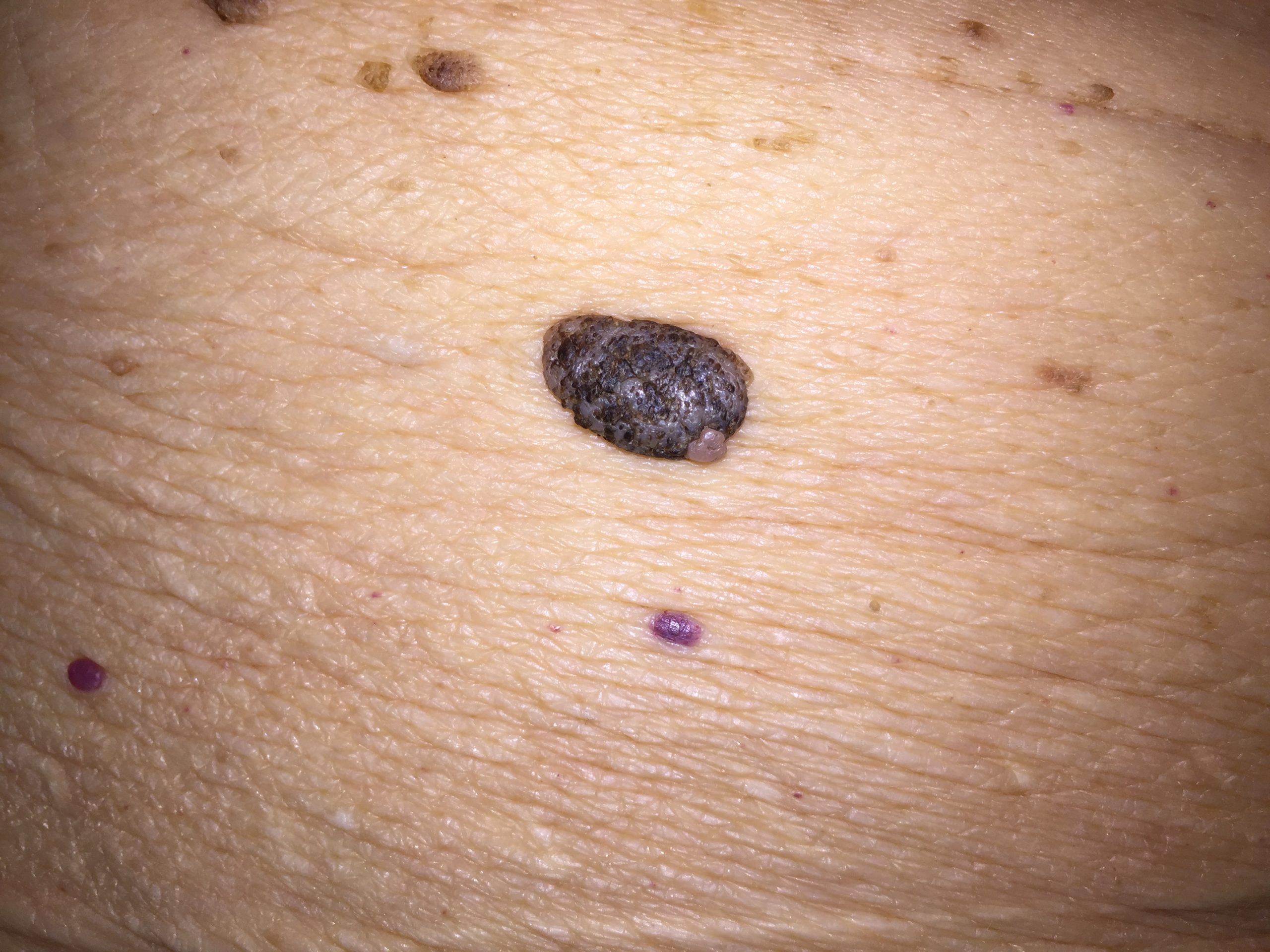
Neoplastics (abnormal growths) and cancer Benign are very common. Some abnormal growths are benign (non-cancerous). However, some neoplasms become and require intervention. |
Benign: Freckles, , , , , wart, . Malignant: , , , .
Seborrheic keratosis (the large brown raised lesion). |
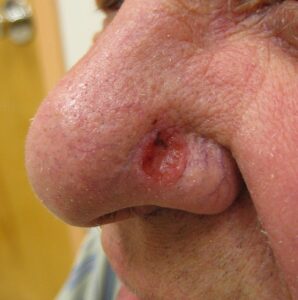
Varies depending on the underlying cause, e.g., spots on the skin, palpable mass, depression of the skin. Basal cell carcinoma.
(Attribution: Photo by James Heilman, MD – Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia. |
|
Skin disorders caused by external agents Cutaneous adverse reactions can occur because of reactions to drugs or other external agents. Adverse reactions can also occur from heat and cold exposures. |
Steven-Johnson syndrome and |
Skin reactions like rashes that start after exposure to external agents like medications. |
*genetic disorders not listed
Clinical Tip
Did you know that some dermatological conditions are emergencies? For example, necrotizing fasciitis (a rare bacterial infection also known as flesh-eating disease) can spread very quickly throughout the body, at a rate of 1 inch per hour. Symptoms include erythema, warmth to the touch, swelling, severe pain, and fever. If not treated immediately, it can lead to , , organ failure, and even death. As a nurse, you must report these findings to the physician or nurse practitioner so immediate treatment can be started.
Knowledge Bites: Pathophysiology
How do you distinguish between common viral and bacterial infections? Common characteristics of a bacterial infection are inflammation, (such as pus), erythema, swelling, pain, odour. Common characteristics of a viral infection are a grouping/cluster of lesions, generally asymmetrical (one side of body), and specific regions on the body (e.g., mouth, nose, feet, hands).
Activity: Check Your Understanding
Name the integument pathophysiology images:
sometimes referred to as oil glands and produce and secrete sebum (a protective substance that helps retain moisture) all over the body except the palms of hands and the soles of feet.
is excessive perspiration.
a discolouration that can appear as a grey/white shade with people of darker skin tones and a dusky bluish/purple shade in people with yellow and lighter skin tones, often visualized in the extremities (fingertips, toes, palms of hands, and soles of feet), conjunctiva and circumoral (around lips) and mucous membranes. Often caused by lack of oxygen in the blood and issues with tissue perfusion caused by conditions related to the respiratory, cardiovascular, and peripheral vascular systems.
is a discolouration that can appear as a grey shade to the mucous membranes/lips, nail beds, extremities in people with darker skin tones, a yellowish shade in people with lighter brown skin, a pale whitish shade in people with lighter skin tones, and a white or very pale pink conjunctiva in all people. The discolouration reflects a combination of the client’s normal skin colour and the connective tissue (white) with the lack of oxygenated hemoglobin due to many states when the sympathetic nervous system is activated (with stress), hypothermia, shock, and anemia. Pallor affects the integument colour because blood is shunted towards the vital organs.
are a highly infectious viral infection characterized by a fever and a rash.
refers to something that is mild, non-invasive and doesn't spread (i.e., non-cancerous)
viral infection that can cause a painful rash.
is an area of the skin that follows a single spinal nerve root.
is a skin condition that causes a rash, scaling, and itching.
is a skin condition that causes dry skin and inflammation.
is a condition that mainly affects the scalp, causing scaly patches and inflammation.
is a chronic skin condition characterized by patches of depigmented skin.
is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation.
is hair loss.
to set clear and obvious borders of where the condition starts and ends
are red, benign growths on skin made of blood vessels.
is another term for itchiness.
is a chronic condition causing itching.
a term indicating something related to the skin.
an abnormal growth.
refers to abnormal cell division (i.e., cancer).
is a small patch of skin that is darker than surrounding skin.
is dark brown pigmented skin/spot present at birth.
is a mole.
is a benign growth associated with aging.
are encapsulated sacs under the skin filled with material, fluid or gas.
is a mole with irregular features.
is a type of skin cancer, commonly found on the face.
is a type of skin cancer.
is an aggressive and severe type of skin cancer.
is a life-threatening bodily response to infection that can lead to tissue damage.
is a life-threatening state whereby the body is not getting enough blood flow.
is fluid seeping from a lesion.