Measurement Systems
Metric system (SI – international system of units): the most widely used system of measurement in the world. It is based on the basic units of meter, kilogram, second, etc.
SI common units:
| Quantity | Unit | Unit symbol |
| Length | meter | m |
| Mass (or weight) | gram | kg |
| Volume | litre | L |
| Time | second | s |
| Temperature | degree (Celsius) | °C |
Metric prefixes (SI prefixes): large and small numbers are made by adding SI prefixes, which is based on multiples of 10.
Metric conversion table:
| Prefix | Symbol (abbreviation) | Power of 10 | Multiple value | Example |
| mega | M | 106 | 1,000,000 | 1 Mm = 1,000,000 m |
| kilo- | k | 103 | 1,000 | 1 km = 1,000 m |
| hecto- | h | 102 | 100 | 1 hm = 100 m |
| deka- | da | 101 | 10 | 1 dam = 10 m |
| meter/gram/litre | 1 | |||
| deci- | d | 10-1 | 0.1 | 1 m = 10 dm |
| centi- | c | 10-2 | 0.01 | 1 m = 100 cm |
| milli- | m | 10-3 | 0.001 | 1 m = 1,000 mm |
| micro | µ | 10-6 | 0.000 001 | 1 m = 1,000,000 µm |
Metric prefix for length, weight and volume:
| Prefix | Length (m – meter) | Weight (g – gram) | Liquid volume (L – litre) |
| mega (M) | Mm (Megameter) | Mg (Megagram) | ML (Megalitre) |
| kilo (k) | km (Kilometer) | kg (Kilogram) | kL (Kilolitre) |
| hecto (h) | hm (hectometer) | hg (hectogram) | hL (hectolitre) |
| deka (da) | dam (dekameter) | dag (dekagram) | daL (dekalitre) |
| meter/gram/litre | m (meter) | g (gram) | L (litre) |
| deci (d) | dm (decimeter) | dg (decigram) | dL (decilitre) |
| centi (c) | cm (centimeter) | cg (centigram) | cL (centilitre) |
| milli (m) | mm (millimeter) | mg (milligram) | mL (millilitre) |
| micro (µ) | µm (micrometer) | µg (microgram) | µL (microlitre) |
Steps for metric conversion:
- Identify the number of places to move the decimal point.
– Convert a smaller unit to a larger unit: move the decimal point to the left.
– Convert a larger unit to a smaller unit: move the decimal point to the right.
Example 1.3.1
326 mm = (?) m
- Identify mm (millimeters) and m (meters) on the conversion table.
Count places from mm to m: 3 places left
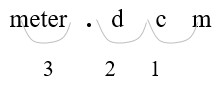
- Move 3 decimal places. (1 m = 1000 mm)
Convert a smaller unit (mm) to a larger (m) unit: move the decimal point to the left.
| 326. mm = 0.326 m | Move the decimal point three places to the left (326 = 326.). |
Example 1.3.2
4.675 hg = (?) g
- Identify hg (hectograms) and g (grams) on the conversion table.
Count places from hg to g: 2 places right
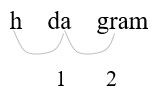
- Move 2 decimal places. (1 hg = 100 g)
Convert a larger unit (hg) to a smaller (g) unit: move the decimal point to the right.
| 4.765 hg = 476.5 g | Move the decimal point two places to the right. |
The Unit Factor Method
Convert units using the unit factor method (or the factor-label method)
- Write the original term as a fraction (over 1).
- Write the conversion formula as a fraction
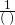 or
or 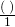 .
.
- Put the desired or unknown unit on the top.
- Multiply the original term by
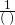 or
or 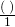 . (Cancel out the same units).
. (Cancel out the same units).
Example 1.3.3
1200 g = (?) kg
- Write the original term (the left side) as a fraction:
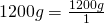
- Write the conversion formula as a fraction. 1 kg = 1000 g:
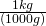
- “kg” is the desired unit.
- Multiply:
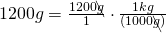 The units “g” cancel out.
The units “g” cancel out.
![]()
![]()
Example 1.3.4
30 cm = (?) mm
- Write the original term (the left side) as a fraction:
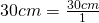
- Write the conversion formula as a fraction. 1 cm = 10 mm:
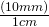
“mm” is the desired unit.
- Multiply:
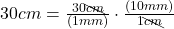 The units “cm” cancel out.
The units “cm” cancel out.
![]()
![]()
Adding and subtracting SI measurements:
Example 1.3.5
Combine after converting to the same unit.
| 3 m | 3000 mm | 1 m = 1,000 mm | |
| – 2000 mm | ——–> | – 2000 mm | |
| 1000 mm |
| 25 kg | 25000 g | 1 kg = 1000 g | |
| + 4 g | ——–> | + 4 g | |
| 25004 g |
The Relationship between mL, g and cm3
How are mL, g, and cm3 related?
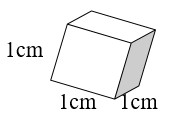
- A cube takes up 1 cm3 of space (1 cm × 1 cm × 1 cm = 1cm3).
- A cube holds 1 mL of water and has a mass of 1 gram at 4°C.
- 1 cm3 = 1 mL = 1 g
Example 1.3.6
Convert.
| 1) 16cm3 = ( ? ) g | |
| 16cm3 = 16 g | 1 cm3 = 1 g |
| 2) 9 L = ( ? ) cm3 | |
| 9 L = 9000 mL | 1 L = 1,000 mL |
| = 9000 cm3 | 1 mL = 1 cm3 |
| 3) 35 cm3 = (?) cL | |
| 35cm3 = 35 mL | 1 cm3 = 1 mL |
| = 3.5 cL | move 1 decimal place left. |
| 4) 450 kg = (?) L | |
| 450 kg = 450,000 g | 1 kg = 1,000 g |
| = 450,000 mL | 1 g = 1 mL |
| = 450 L | 1 L = 1,000 mL |
Example 1.3.7
A swimming pool measures 10 m by 8 m by 2 m. How many kilolitres of water will it hold?
| V = w l h = (8m) (10m) (2m) = 160 m3 | 160 m3 = ( ? ) kL |
| 160m3 = 160,000,000 cm3 | 1 m = 100 cm, 3 × 2 = 6, move 6 places right for volume. |
| 160,000,000 cm3 = 160,000,000 mL | 1 mL = 1 cm3 |
| 160,000,000 mL = 160 kL | 1 kL = 1,000,000 mL |
| 160 m3 = 160 kL | The swimming pool will hold 160 kL of water. |
Practice questions
1. Convert each of the following measurements:
a. 439 mm = ( ? ) m
b. 48.3 mL = ( ? ) kL
c. 7230 g = ( ? ) kg
d. 52 cm = ( ? ) mm
2. Combine:
a. 7 m – 3000 mm = ( ? ) mm
b. 63 kg + 6 g = ( ? ) g
3. Complete:
a. 38 cm3 = ( ) g
b. 5 L = ( ) cm3
c. 18 L of water has a volume of ___________ cm3 .
d. A water tank measures 45 cm by 35 cm by 25 cm. How many kilolitres of water will it hold?

