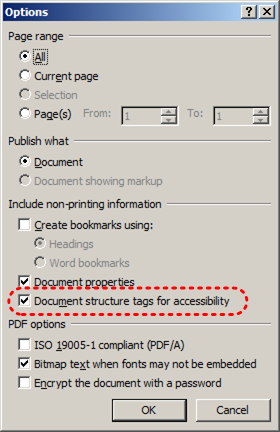
WCAG 2.0 Applicability:
- 1.3.1 Info and Relationships
- 1.3.2 Meaningful Sequence
- 2.4.2 Page Titled
 Curb Cuts:
Curb Cuts: Using built-in structural features is much more reliable that trying to use typography for formatting (e.g. tabs to separate table cells, repeated new lines for a page break).
6.1 Tables
When using tables, it is important to ensure that they are clear and appropriately structured. This helps all users to better understand the information in the table and allows assistive technologies (e.g. screen readers) to provide context so that the information within the table can be conveyed in a meaningful way.
Tips for tables
- Only use tables for tabular information, not for formatting, such as to position columns.
- Use “real tables” rather than text formatted to look like tables using the TAB key or space bar. These will not be recognized by assistive technology.
- Keep tables simple by avoiding merged cells and dividing complex data sets into separate smaller tables, where possible.
- If tables split across pages, set the header to show at the top of each page. Also set the table to break between rows instead of in the middle of rows.
- Create a text summary of the essential table contents. Any abbreviations used should be explained in the summary.
- Table captions or descriptions should answer the question “what is the table’s purpose and how is it organized?” (e.g. “A sample order form with separate columns for the item name, price and quantity”).
- Table cells should be marked as table headers when they serve as labels to help interpret the other cells in the table.
- Table header cell labels should be concise and clear.
- Ensure the table is not “floating” on the page (see Technique 4. Avoid “Floating” Elements).
To add a table with headings
- Go to menu item: Insert.
- In the Tables section, select the Tables icon.
- Select the number of rows and columns you would like your table to have.
- Select the table and a Table Tools menu item should appear.
- Go to menu item: Table Tools > Design.
- In the Table Style Options section, select the Header Row check boxNote: Whenever possible, keep tables simple with just one row of headings.
6.2. Lists
When you create lists, it is important to format them as “real lists”. Otherwise, assistive technologies will interpret your list as a series of short separate paragraphs instead of a coherent list of related items.
To create an ordered or unordered list
- Go to menu item: Home.
- In the Paragraph section, select the Bullets icon for unordered lists or select the Numbering icon for ordered lists.
- To choose a different list format, select the arrow beside the icon.
- Select a format from the format Library that appears in the drop-down menu.
To modify list styles
- Go to menu item: Home.
- In the Paragraph section, select the arrow beside the Bullets icon for unordered lists or select the arrow beside the Numbering icon for ordered lists.
- Select Define New Bullet… to create a new unordered list format.
- Select Define New Number Format… to create a new ordered list format.
- In the New Bullet dialog or the New Number Format dialog, select the list characteristics.
- Select OK.
6.3 Columns
Use the Columns feature for placing text in columns.
Note: Because columns can be a challenge for some users with disabilities (e.g., people using magnifiers), consider whether a column layout is really necessary.
6.4 Page Breaks
Start a new page by inserting a page break instead of repeated hard returns.
To add a page break
- Go to menu item: Page Layout.
- In the Page Setup section, select the arrow beside the Breaks icon.
- Select the type of break to add. Page break is used to start a new page with the same page layout (page orientation, headers, page numbering, etc.). Section break is used if you want to start a new section of the document with a differing page layout.
6.5 Table of Contents
Creating an index or table of contents to outline office document content can provide a means of navigating the meaningful sequence of content.
The best way to generate a table of contents is after applying the predefined heading styles, such as “Heading 1” as described above, to the headings that you want to include in your table of contents. After you apply these styles, you can then create a table of contents.
To insert a table of contents
- Place the cursor in your document where you want to create the table of contents.
- Go to menu item: References.
- In the Table of Contents section, select Table of Contents.
- Select the style that you want to use.
To update a table of contents
- Select the table.
- Go to menu item: References.
- In the Table of Contents section, select the Update Table button.
6.6 Page Numbering
Numbering the pages of you document helps those reading and editing your document effectively navigate and reference its content. For users of assistive technologies, it provides a valuable point of reference within the document.
To insert page numbers
- Go to menu item: Insert.
- In the Header & Footer section, select Page Number.
- Select where you would like to insert your page numbers.
- Select the style of page number you would like to use.
To format page numbers
- Go to menu item: Insert.
- In the Header & Footer section, select Page Number.
- Select Format Page Numbers…
- In the Page Number Format dialog, select the page format characteristics you would like to use
Note: These changes are applied to the predefined page format styles. It does not create a new page format style.
6.7 Document Title
In case the document is ever converted into HTML, it should be given a descriptive and meaningful title.
To change the title of the current document
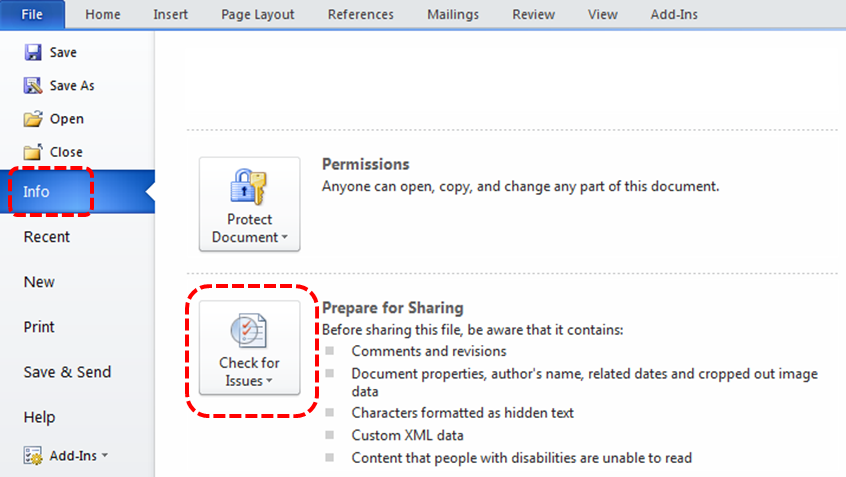
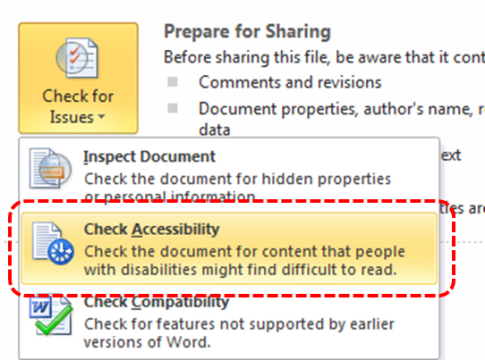
- Go to menu item: File.
- Select Info from the list in the left window pane.
- In the right window pane, select on the Title text box.
- Enter the TitleNote: The Title defined in the properties is different than the file name. It is also unrelated to the template name, discussed above.