1.1. Introduction to Algebra
Introduction
Review of basic algebraic terms:
| Algebraic term | Description | Example |
| Algebraic expression | A mathematical phrase that contains numbers, variables (letters), and arithmetic operations (+, – , ×, ÷, etc.). |
3x – 4 5a2 – b + 3 12y3 + 7y2 – 5y + |
| Constant | A number on its own. | 2y + 5 constant: 5 |
| Coefficient | The number in front of a variable. |
-9x2 coefficient: -9 x coefficient: 1 (x = 1 · x) |
|
Term |
A term can be a constant, a variable, or the product of a number and variable. (Terms are separated by a plus or minus sign.) |
2x3 + 7x2 – 9y – 8 Terms: 2x3, 7x2, – 9y, –8 |
| Like terms | The terms that have the same variables and exponents (differ only in their coefficients). |
2x and -7x -4y2 and 9y2 0.5pq2 and |
Polynomial: an algebraic expression that contains one or more terms.
Example: 7x , 5ax – 9b , 6x2 – 5x + ![]() , 7a2 + 8b + ab – 5
, 7a2 + 8b + ab – 5
There are special names for polynomials that have one, two, or three terms:
- Monomial: an algebraic expression that contains only one term.
Example: 9x , 4xy2 , 0.8mn2 , ![]() a2b
a2b
- Binomial: an algebraic expression that contains two terms.
Example: 7x + 9 , 9t2 – 2t , 0.3y + ![]()
- Trinomial: an algebraic expression that contains three terms.
Example: ax2 + bx + c , – 4qp2 + 3q + 5
Combining Terms
Like terms: terms that have the same variables and exponents (the coefficients can be different).
Examples:
| Example | Like or unlike terms |
| 7y and -9y | Like terms |
| 6a2, -32a2, and –a2 | Like terms |
| 0.3 x2y and -48x2y | Like terms |
| Like terms | |
| -8y and 78x | Unlike terms |
| 6m3 and -9m2 | Unlike terms |
| -9u3w2 and -9w3u2 | Unlike terms |
Combine like terms: add or subtract their coefficients and keep the same variables and exponents.
Note: unlike terms cannot be combined.
Example 1.1.1
| 1) 3a + 7b – 9a + 15b = (3a – 9a) + (7b + 15b) | Regroup like terms. |
| = -6a + 22b | Combine like terms. |
| 2) 2y2 – 4x + 3x – 5y2 = (2y2 – 5y2) + (-4x + 3x) | Regroup like terms. |
| = -3y2 – 1x | Combine like terms. |
| = -3y2 – x |
| 3) 8xy2 – x2y + 4x2y – 6xy2 | |
| = 8xy2 – x2y + 4x2y – 6xy2 | Or underline like terms without regrouping. |
| = 2xy2 + 3x2y | Combine like terms. |
| 4) 2(2m + 3n) + 3(m – 4n) = 4m + 6n + 3m – 12n | Distributive property. |
| = 7m – 6n | Combine like terms. |
Removing Parentheses
If the sign preceding the parentheses is positive (+), do not change the sign of terms inside the parentheses, just remove the parentheses.
If the sign preceding the parentheses is negative (-), remove the parentheses and the negative sign (in front of parentheses), and change the sign of each term inside the parentheses.
Remove parentheses:
| Algebraic expression | Remove parentheses | Example |
| (ax + b) | ax + b | (5x + 2) = 5x + 2 |
| (ax – b) | ax – b | (9y – 4) = 9y – 4 |
| – (ax + b) | -ax – b | – ( |
| – (ax – b) | -ax + b | – (0.5b – 2.4) = -0.5b + 2.4 |
Example 1.1.2
| 1) 9x2 + 7 – (2x2 – 2) = 9x2 + 7 – 2x2 + 2 | Remove parentheses. |
| = 7x2 + 9 | Combine like terms. |
| 2) (-8y + 5z) – 4(y – 7z) = -8y + 5z – 4y + 28z | Remove parentheses. |
| = -12y + 33z | Combine like terms. |
| 3) – (3a2 + 4a – 4) + 3(4a2 – 6a + 7) | Remove parentheses. |
| = – 3a2 – 4a + 4 + 12a2 – 18a + 21 | Distributive property. |
| = 9a2 – 22a + 25 | Combine like terms. |
| 4) -5(u2 – 3u) + 3(2u – 4) – (5 – 3u + 4u2) | Distributive property. |
| = -5u2 + 15u + 6u – 12 – 5 + 3u – 4u2 | Remove parentheses. |
| = -9u2 + 24u – 17 | Combine like terms. |
Multiplying and Dividing Algebraic Expressions
Multiplying a monomial and a polynomial:
- Use the distributive property: a (b + c) = ab + ac
- Multiply coefficients and add exponents with the same base. Apply am an = am+n
Example 1.1.3
| 1) 3x3 (5x2 – 2x) = (3x3) (5x2) – (3x3) (2x) | Distributive property: a (b + c) = ab + ac |
| = (3 ∙ 5) (x3 x2) – (3 ∙ 2) (x3 x1) | Regroup x = x1 |
| = 15 (x3+2) – 6 (x3+1) | Multiply the coefficients & add the exponents. |
| = 15x5 – 6x4 | am ∙ an = am+n |
| 2) 5ab2 (2a2b +ab2 – a) | Distribute. |
| = (5ab2) (2a2b) + (5ab2) (ab2) + (5ab2) (-a) | Multiply the coefficients and add exponents. |
| = (5 ∙ 2) (a1+2 b2+1) + (5a1+1 b2+2) – (5a1+1b2) | b = b1 , a = a1 |
| = 10a3b3 + 5a2b4 – 5a2b2 | am ∙ an = am+n |
Dividing a polynomial by a monomial:
- Split the polynomial into several parts.
- Divide a monomial by a monomial. Apply
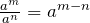 .
.
Example 1.1.4
![]()
Steps Solution
- Split the polynomial into three parts:
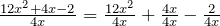
- Divide a monomial by a monomial:
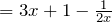
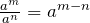
The FOIL method: an easy way to find the product of two binomials (two terms).
| (a + b) (c + d) = ac + ad + bc + bd F O I L |
Example |
| F – First terms | first term × first term (a + b) (c + d) | (x + 5) (x + 4) |
| O – Outer terms | outside term × outside term (a + b) (c + d) | (x + 5) (x + 4) |
| I – Inner terms | inside term × inside term (a + b) (c + d) | (x + 5) (x + 4) |
| L – Last terms | last term × last term (a + b) (c + d) | (x + 5) (x + 4) |
| FOIL method | Example |
| (a + b) (c + d) = ac + ad + bc + bd | (x + 5) (x + 4) = x ∙ x + x ∙ 4 + 5x + 5 ∙ 4 = x2 + 9x + 20 |
| F O I L | F O I L |
Multiplying binomials (2 terms × 2 terms):
Example 1.1.5
| 1) F O I L |
The FOIL method. |
| Combine like terms. |
| 2) |
FOIL |
| Combine like terms. |
| 3) |
FOIL |
| Combine like terms. |
| 4) |
FOIL |
| Combine like terms. |
Practice questions
1. Identify the terms of each polynomial:
a. 5x3 + 8x2 + 2x
b. –![]() y4 + 9a2 + a – 1
y4 + 9a2 + a – 1
2. Combine like terms:
a. 7x + 10y – 8x + 9y
b. 12a2 – 33b + 2b – 6a2
c. 13n + 5(6n – m2) + 7(2m2 + 3n)
3. Simplify:
a. 15a2 + 9 – (5a2 – 4)
b. (-13x + 9y) – 6(x – 5y)
c. 5(ab – 2xy) – 6(-2ab + 3xy)
d. (5y – 7) (8y + 9)
e. (7r – 2t) (3r + 4t2)
f. (x – ![]() ) (x –
) (x – ![]() )
)

