Hypertension and Dyslipidemia
Background
Page Contents
The Cardiovascular System
The role of the cardiovascular system is to:
- regulate blood flow to tissues in the body
- deliver oxygenated blood and nutrients
- retrieve waste products
- regulate the temperature of the body
- transport hormones
- maintain fluid volume
- regulate pH
- facilitate gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
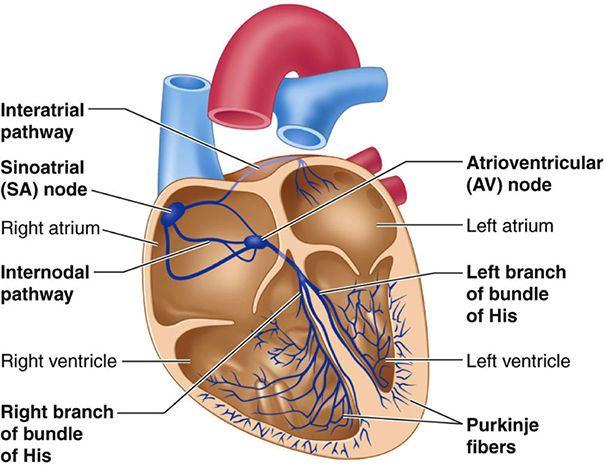
Electrical Conduction of the Heart
The diagram of the heart below provides an overview of the different parts of the heart, and how blood flows through it.
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is a group of disorders involving the heart and blood vessels.
Common forms of CVD include:
- Coronary artery disease ()
- Hypertension (HTN)
- Heart failure
- Ischemic heart disease or coronary heart disease ()
- Peripheral arterial disease ()
- Dyslipidemia
In this section we will focus on Hypertension and Dyslipidemia.
Hypertension
Hypertension is a medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated.
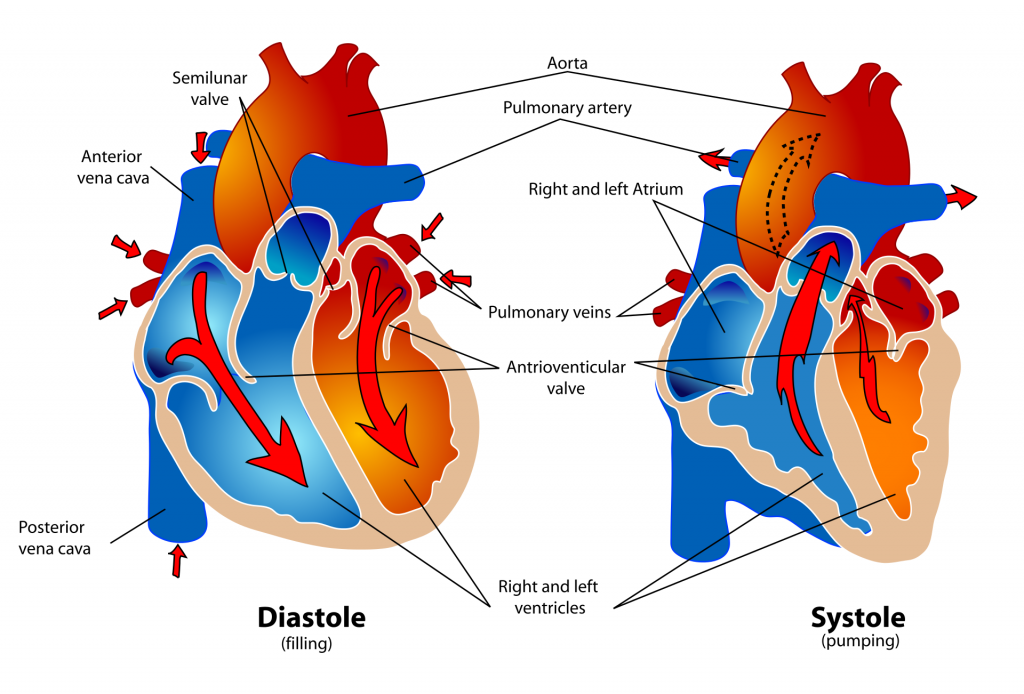
The cardiac cycle consists of two phases: systolic and diastolic. Systolic blood pressure measurement is the force exerted on the walls of blood vessels during contraction (when the heart beats). Diastolic blood pressure measurement is the force exerted during relaxation (resting between beats).
Blood Pressure (BP) is regulated by:
- Cardiac output
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Renin angiotensin aldosterone system ()
- Renal function
Diastole and Systole
It’s important to understand the various physiological mechanisms involved in blood pressure regulation as cardiac medications act on those systems.
Dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia is an abnormal amount of lipids in the blood, which is confirmed using a blood test.
The main lipids involved include:
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
- Triglycerides (TG)
- Hyperlipidemia: abnormally high levels of TC, LDL-C or TG
- Hypercholesterolemia: elevated TC and/or LDL-C
A diagnosis of dyslipidemia can also mean that HDL cholesterol levels are too low.
Atherosclerosis and Coronary Artery Disease
- Coronary arteries (CAD)
- Heart (myocardial infarction)
- Brain (stroke)
- Legs (PAD)
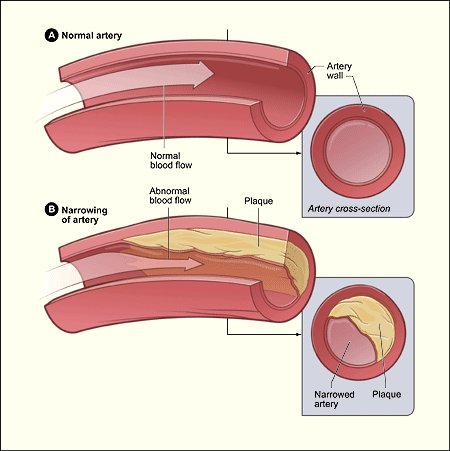
Coronary artery disease: disruption of blood flow due to the build up fatty substances in the coronary arteries
Coronary heart disease/Ischemic heart disease: weakening of the heart caused by reduced blood flow to the heart
Peripheral arterial disease: narrowed arteries reducing blood flow to arms or legs
Renin angiotensin aldosterone system: regulation of blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance

